Global historical CO₂ emissions from fossil fuels and industry 1750-2023
In 2023, global carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuel combustion and industrial processes reached a record high of 37.8 billion metric tons (GtCO₂). Global CO₂ emissions are projected to have reached record levels in 2024. The world has pumped more than 1,800 GtCO₂ into the atmosphere since the industrial revolution began, though almost 45 percent has been produced since 2000.
What is carbon dioxide?
CO₂ is a colorless, naturally occurring gas that is released after people and animals inhale oxygen. It is a greenhouse gas, meaning it absorbs and releases thermal radiation which in turn creates the “greenhouse effect”. In addition to other greenhouse gases, CO₂ is also a major contributor to the ability of the Earth to maintain a habitable temperature. Without CO₂ and other greenhouse gases, Earth would be too cold to live on. However, while CO₂ alone is not a harmful gas, the abundance of it is what causes climate change. The increased use of electricity, transportation, and deforestation in human society have resulted in the increased emissions of CO₂, which in turn has seen a rise in earth’s temperature. In fact, around 70 percent of global warming since 1851 is attributable to CO₂ emissions from human activities.
Who are the largest emitters worldwide?
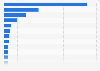
China is the biggest carbon polluter worldwide, having released almost 12 GtCO₂ in 2023. This was more than the combined emissions of the United States and India, the second and third-largest emitters that year, respectively.